Backend Development
We use Java based framework to develop monolith and micro-service architectue based server-side applications.
Spring Boot
Spring Boot is Spring's convention-over-configuration solution for creating stand-alone, production-grade Spring-based Applications that you can "just run". It is preconfigured with the Spring team's "opinionated view" of the best configuration and use of the Spring platform and third-party libraries so you can get started with minimum fuss.


Grails
Grails is an open source web application framework that uses the Apache Groovy programming language (which is in turn based on the Java platform). It is intended to be a high-productivity framework by following the "coding by convention" paradigm, providing a stand-alone development environment.
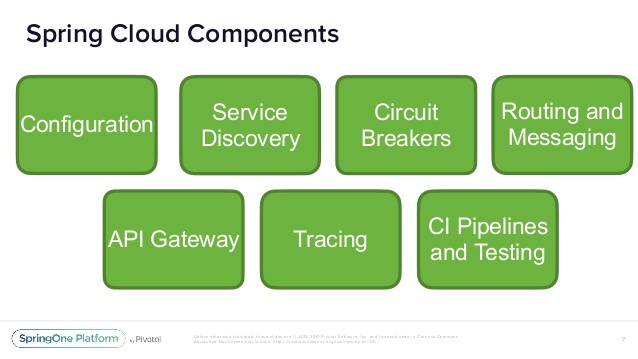
Spring Cloud
Spring Cloud provides tools for developers to quickly build some of the common patterns in distributed systems (e.g. configuration management, service discovery, circuit breakers, intelligent routing, micro-proxy, control bus, one-time tokens, global locks, leadership election, distributed sessions, cluster state). Coordination of distributed systems leads to boiler plate patterns, and using Spring Cloud developers can quickly stand up services and applications that implement those patterns.
Micronaut
Micronaut is a JVM-based framework for building lightweight, modular applications. Developed by OCI, the same company that created Grails, Micronaut is the latest framework designed to make creating microservices quick and easy.
JVM Languages
A core feature of the JVM languages is the cross-platform portability, which means that programs written on one platform are executable on any combination of software and hardware with adequate runtime support. This is achieved by compiling code into bytecode first, instead of directly to platform-specific machine code.
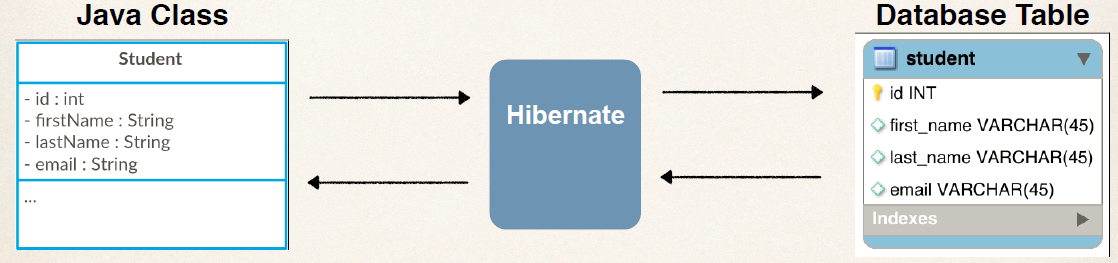
Object Relational Mapping(ORM)
Object-relational mapping is simply the process of persisting any Java object directly to a database table. Usually, the name of the object being persisted becomes the name of the table, and each field within that object becomes a column. With the table set up, each row corresponds to a record in the application.
